One of the benefits of Microsoft 365/ Microsoft Endpoint is the interaction across all the different products. With the connection between multiple products. I want to show how you can use multiple products from Microsoft to block apps with a Low Reputation or Upload to a new detected cloud provider.
A good example is the integration between Microsoft Defender, Security protection features on Windows 10 endpoints, and integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint/ Cloud App Security. All the features are connected and linked. Through the integration of Microsoft Cloud App Security (MCAS) and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, it is possible to block access to certain URLs or IP addresses.
Based on the information available in Cloud App Security, the app’s domains are used to create domain indicators in the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint portal. Windows Defender blocks the apps with the Exploit Guard Network Policy. The result; 
For example to block apps with a Low Reputation or upload to a newly detected cloud provider; the following tools are used:
- Microsoft Endpoint Manager; For the settings on the cliënt
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint; For the interaction with Microsoft Cloud App Security
- Microsoft Cloud App Security; For the app protection and detected data based on low reputation and newly detected providers.
For Microsoft Cloud App Security and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint you need to have a Microsoft 365 E5 license.
There are some prerequisites; for more information see -> Information Microsoft
In short, you need minimal;
- Microsoft Cloud App Security license
- Microsoft Defender ATP license
- Windows 10 version 1709 (OS Build 16299.1085 with KB4493441), Windows 10 version 1803 (OS Build 17134.704 with KB4493464), Windows 10 version 1809 (OS Build 17763.379 with KB4489899) or later Windows 10 versions
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Editorial note; The post is based on the new Microsoft 365 naming convention.
- Microsoft 365 Defender (previously Microsoft Threat Protection).
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (previously Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection).
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (previously Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection).
- Microsoft Defender for Identity (previously Azure Advanced Threat Protection).
Microsoft Endpoint Manager Client settings
For network protection, we are going to configure a Device Configuration Policy in Microsoft Endpoint Manager with a target to the devices. The settings are based on the Endpoint Protection and Device Restrictions settings.
Configuration
- Go to Microsoft Endpoint Manager
- Open Devices (10)
- Click on Configuration Profile (11)
- Click on Create profile (12)
- Select platform; Windows 10 and later (13)
- Select profile Device restrictions (14)

Configure the following settings;
Enable Real-Time monitoring and Behavior monitoring as a minimal setting. Of course, you can enable more features to secure the workspace. The settings listed in red are a minimal requirement for blocking apps based on MCAS data.
Enable cloud-delivered protection

For Prompt users before sample submission, select Send all data without prompting or Send all samples automatically.

Now we need to configure the network filtering option. For configuring the network filtering create a new profile and select as profile; Endpoint Protection.
To block outbound connection from any app to low reputation IP/domain or URL enable the Network protection setting. It is recommended to use Network Protection first in audit mode to test the outcome.

Now deploy both profiles to a user or device group from Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint configuration for interaction between MCAS and Defender for Endpoint
Next for the integration, you need to set up the interaction between MCAS and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
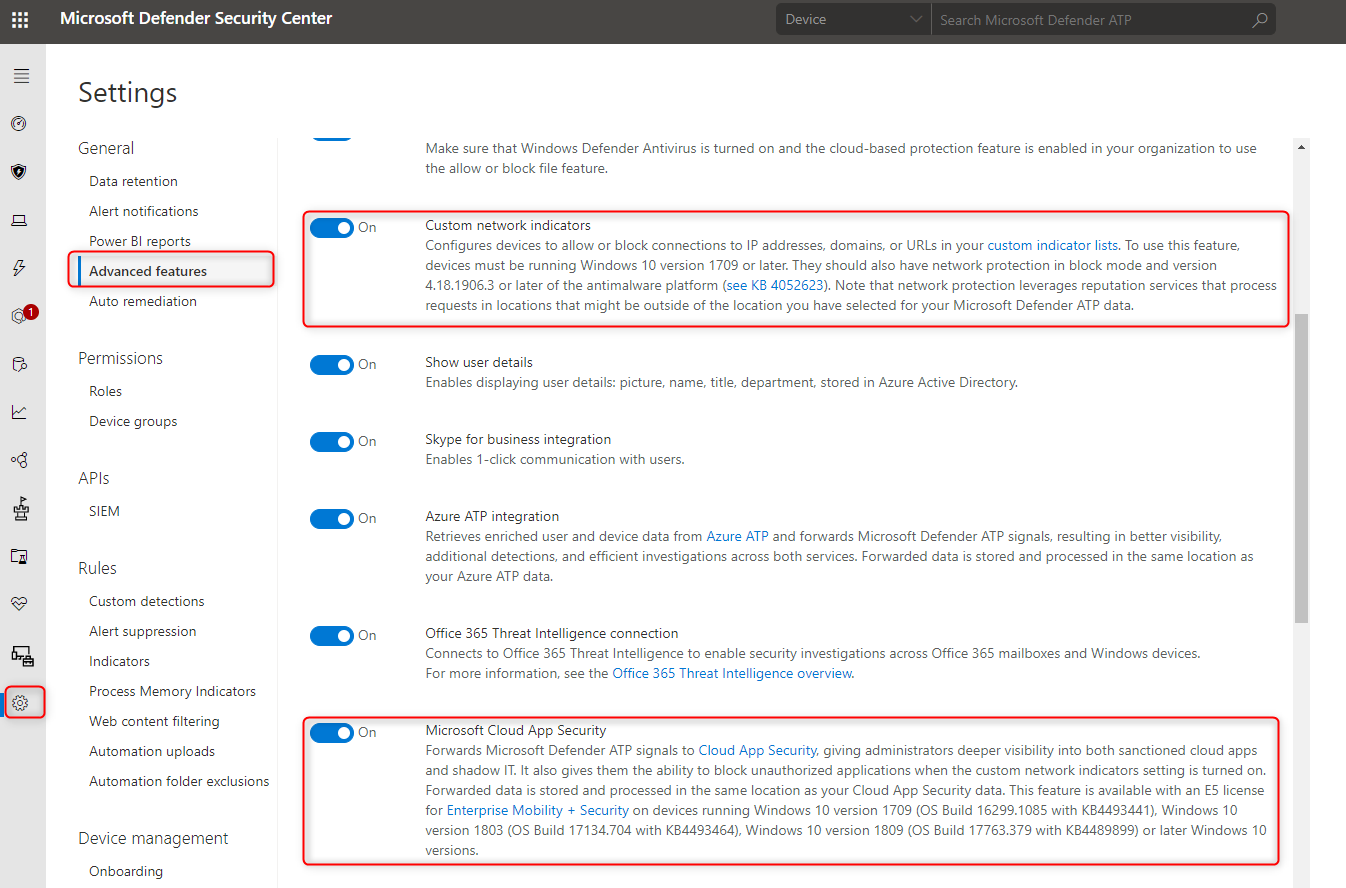
- Open Microsoft Defender for Endpoint portal
- Go to Settings -> Advanced Features
Now activate the Custom network indicators and Microsoft Cloud App Security integration. For the Custom network indicators, a requirement is minimal Windows 10 1709.
MCAS configuration for pushing unsanctioned apps to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
In Microsoft Cloud App Security MCAS we need to set up the integration to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for blocking unsanctioned apps from Cloud App Security.
- Open the MCAS portal
- Open settings
- Go to Microsoft Defender ATP (3) and enable the setting; Block unsanctioned apps (4)

Now the settings are activated on the endpoint, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint integrates with MCAS and configured for the custom network indicators. The final configuration is to blocking apps from the MCAS portal.
Block apps in MCAS
- Open the Cloud App Security portal
- Go to Cloud app catalog Discover -> Cloud app catalog or Discovered apps
Difference between cloud app catalog and discovered apps
The Cloud Discovery dashboard is designed to give you more insight into how cloud apps are being used in your organization.
The Cloud App Catalog gives you a full picture of what Cloud Discovery identifies. Cloud Discovery analyzes your traffic logs against Microsoft Cloud App Security’s cloud app catalog of over 16,000 cloud apps.
Cloud app catalog

Discovered apps

Go to the Discovered Apps portal in MCAS. If you enabled the integration between Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and MCAS the view is based on used apps in the organization for the last 90 days of information.
The name Win10 Endpoint users is a continuous report that included data from Defender for Endpoint

Click on the Score column to sort the list from 0 upwards and see apps with a low rating. Click the app to view more information and view why the app gets a low score. File Dropper is a good example;
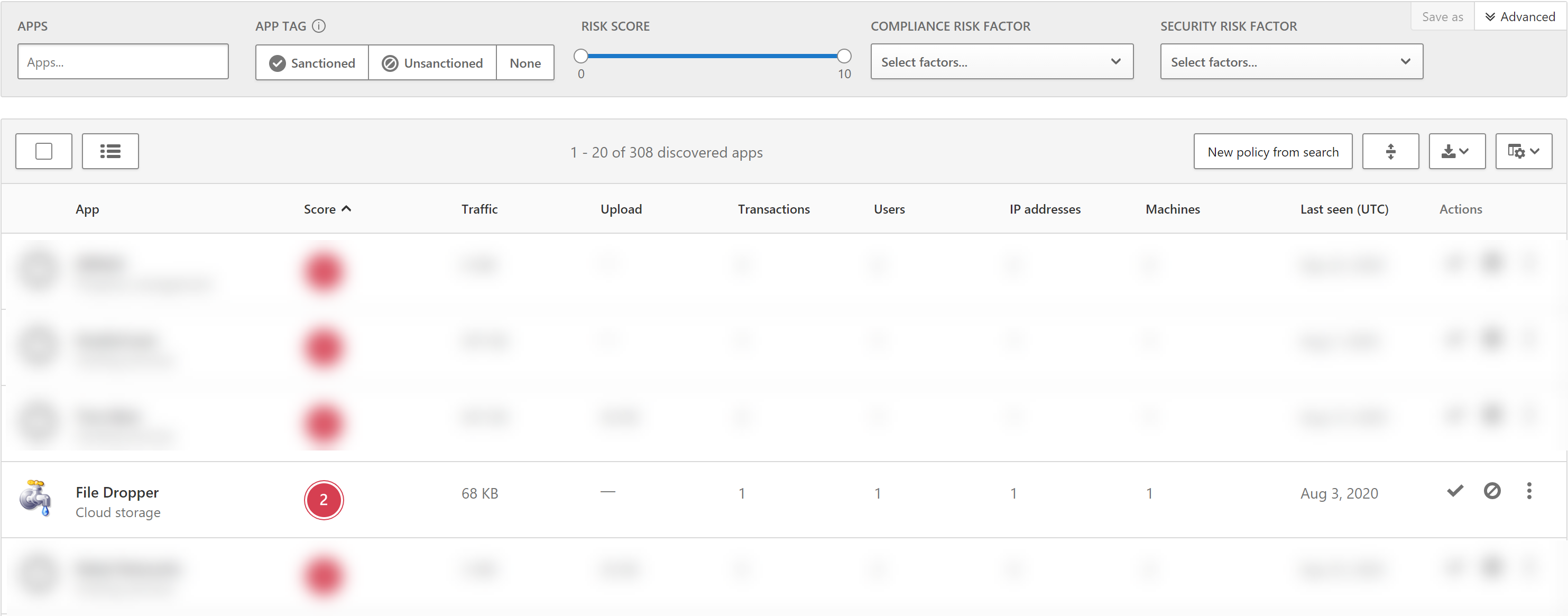
For more information about File Dropper; click on the icon/ title. Now you can see the app information overview page. Here you can find the usage, app info, users, machines, alerts.

The info gives more information about the app and the score

Block apps
For blocking the app. Click the unsanctioned tag under actions:

Now the app is blocked;

After clicking the block button it takes a couple of time before the URLs are listed in the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint portal.
Automatic unsanctioned actions based on risky score and category cloud storage
In addition to manually blocking applications, automatic blocking is even more interesting. In Cloud App Security, you can create a rule that automatically blocks all applications based on a condition.
For example; To automatically unsanctioned any app with a low score (0-2 for example) and listed in the category Cloud storage:
Go to; policy – Create Policy – App discovery policy.
The example in the screenshots detects apps with a risk score 0-2 in the category of cloud storage.

To block the app, it is required to configure the Governance actions: In addition to automatic blocking, it is also possible to approve apps automatically with the rule. For an automatic block; Tag app as unsanctioned

Automatic unsanctioned actions based on newly detected cloud storage
For example; To automatically unsanctioned newly detected cloud storage apps used by more than 50 users with total daily usage of more than 50MB. Go to Control -> Policies and create a new policy based on the template; New cloud storage app.
Shortly after you create this rule apps that fall into the category will be tagged as unsanctioned. Before you enable this rule it would be wise to check the list of apps.

For the alerts and Governance actions:

Check Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Defender for Endpoint listed the app filedropper after the Cloud App Security action.

Device result
Now we open the website Box you will see that it is automatically blocked via Defender SmartScreen.
Microsoft Edge: 
Internet Explorer:
Chrome: 
Incident alerting Security Center
The rule is configured with the option; Alert and Block. After starting the connection to a blocked cloud application. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint created the alert.



Sources:
Microsoft: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/microsoft-defender-atp/microsoft-defender-advanced-threat-protection
Microsoft Cloud App Security: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cloud-app-security/