It is time for part 3D of the ultimate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) series. After Part 3C (Onboard Defender for Endpoint using Azure Arc) it is now time for some more technical deep-dive scoped on onboarding with Configuration Manager aka SCCM and GPO. Part 3D is focused on onboarding using Configuration Manager/ GPO. Ideally use Microsoft Intune for Windows endpoints. Servers can be onboarded with the use of Defender for Cloud and Azure Arc. See parts 3A, 3B, and 3C for the recommended onboarding methods.
Important: Defender AV/ Next Generation Protection onboarding is critical and part of the complete protection platform. All AV/ Next Generation Protection information will be explained more in-depth including migration from other AV states.
NOTE: Blog series focuses on features in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P2 all Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P1 features are available in P2.
Specific question or content idea part of Defender for Endpoint? Use the contact submission form and share the post ideas.
Introduction
Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager or GPO can be used for onboarding Defender for Endpoint. Ideally, migrate machines to Intune or use specific workloads with co-management enabled.
Important announcement for servers
Previously it was possible to use Defender for Endpoint for Server licensing for onboard Windows Server 2008R2 and higher in Defender for Endpoint via GPO, Configuration Manager, or other management toolings. Microsoft updated the docs; with the following information;
Defender for Endpoint Plan 1 and 2 (standalone) don’t include server licenses. To onboard servers, choose form the following options:
Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 1 or Plan 2 as part of the Defender for Cloud offering.
Based on the announcement Microsoft will stop with Defender for Endpoint for Servers offering where Azure Arc/ Defender for Cloud is the only way for onboarding devices in Defender for Endpoint. For Windows Server versions – it is recommended to use Defender for Cloud / Azure Arc – to make sure the product can be licensed in the future. See Part 3B/ 3C for more information and detailed instructions.
Deploy with Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager – using onboarding profile
Defender for Endpoint can be easily deployed with the use of Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager and the pre-created Endpoint Protection onboarding policies for supported Windows 10/11 systems.
Configuration Manager version 1606 and later provides an integrated console to deploy Microsoft Defender for Endpoint policies. When using an older version in production – it is highly recommended to update MECM to one of the latest versions.
Common asked question; is the Endpoint Protection site role needed for deploying Defender for Endpoint to Windows 10/11 workstations?
The answer is no. For the initial deployment, it is not needed to configure the Endpoint Protection site role. For Defender AV the site role can be configured when managing settings with Configuration Manager. Defender AV-related information and the available management options will be explained in one of the next parts. All parts starting with Part 3(letter) is focussing only on Defender for Endpoint onboarding.
Download onboarding file
From within the Microsoft 365 Defender portal, it is possible to download the .onboarding policy file. The .onboarding policy file can be used for Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager current branch and later.
- Go to Security.Microsoft.com -> Settings -> Endpoints -> onboarding
- Under the Deployment method, select Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager
- Download the onboarding package
- Unzip folder – the .onboarding file is needed

Import profile
Now it is needed to create a Windows Defender ATP Policy and upload the downloaded onboarding file in Configuration Manager. In Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, navigate to Assets and Compliance > Overview > Endpoint Protection > Microsoft Defender ATP Policies
Type the Name and Description for the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint policy and select Onboarding. Browse to the .onboarding file extracted from the downloaded .zip file.
Note: Workspace Key and Workspace ID are only needed when using down-level systems installed with the MMA agent. For Windows 10/11 only the configuration file need to be configured.
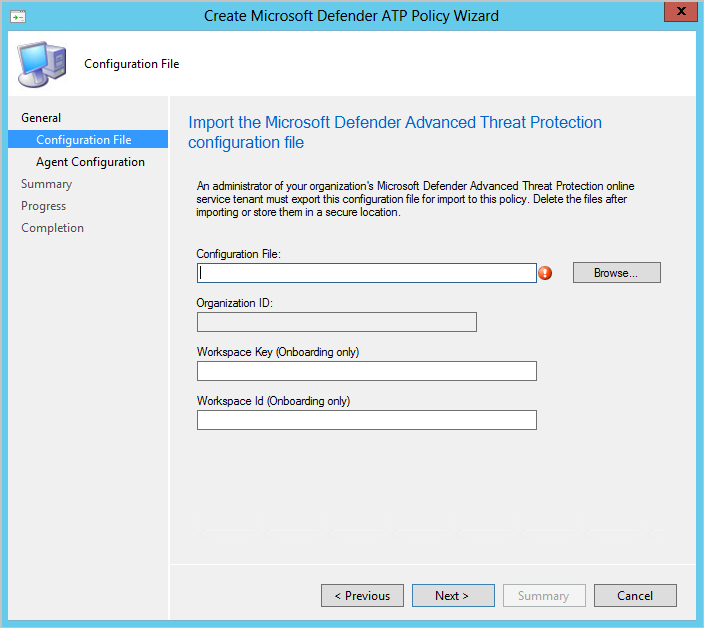
Specify the file samples that are collected and shared from managed devices for analysis, configure the value; all file types
After creating the policy, deploy the policy to one of the available device collections. Test always with some test devices before the initial deployment. After deploying it can take some time before the onboarding process will be launched on the machine.
Deploy with Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager – using Co-Management
When Windows 10/11 systems are currently not onboarded in MEM/ Intune it is possible to onboard the machines with the use of co-management.
Co-management attaches the existing Configuration Manager environment with the Microsoft 365 Cloud. Co-management helps with enabling more cloud-powered features like Intune/ Conditional Access and the management of configurations.

By using co-management there is the flexibility to use multiple solutions and migrate more to the cloud. This blog is not explaining co-management completely in-depth. For more information see: What is co-management? | Microsoft Learn
Workloads
When using Co-management multiple workloads can be used for switching a small set of workloads to Intune or a specific pilot group.
Once Co-management is configured, then navigate to Administration -> Overview -> Cloud Services ->Cloud Attach and open the workloads.
In Configuration Manager it can be configured based on three levels:
- Configuration Manager: Workload will be managed by SCCM only
- Pilot Intune: Workload will be managed with Intune for a specific pilot collection. This way can be used to get more control
- Intune: Workload will be completely managed by Intune only.
There are multiple workloads that can be managed by Intune such as :
- Compliance policies
- Device configuration
- Endpoint Protection
- Resource access policies
- Client apps
- Office Click-to-Run apps
- Windows Update policies
For Defender for Endpoint the Endpoint Protection workloads are needed. Part of the Endpoint Protection workload are the following items;
- Windows Defender Antimalware
- Windows Defender Application Guard
- Windows Defender Firewall
- Windows Defender SmartScreen
- Windows Encryption
- Windows Defender Exploit Guard
- Windows Defender Application Control
- Windows Defender Security Center
- Windows Defender for Endpoint (now known as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint)
Important to know; when using Co-Management and policies are configured in Configuration Manager the policy stays on the device until the Intune policies overwrite the Configuration Manager policies. This is by design and configured for enabling protection during the workload migration. See Co-management workloads for more information.
Deployment profile
For deploying Defender for Endpoint all steps explained in part Onboard using Microsoft Intune – Part3A can be used. Only the device tag is not part of the Endpoint Protection workload, device configuration profiles are part of the Device configuration workload in Configuration Manager.
Onboard using Group Policy
Group Policy can be used for completing the onboarding of Defender for Endpoint.
Download onboarding file
From within the Microsoft 365 Defender portal, it is possible to download the GPO-related onboarding file.
- Go to security.Microsoft.com -> Settings -> Endpoints -> onboarding
- Under Deployment method, select Group Policy
- Download the onboarding package
- Unzip folder – the WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingScript.cmd file is needed. OptionalParamsPolicy contains the additional sample sharing setting.

Copy the WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingScript.cmd file to a shared read-only location that can be accessed by the devices.
Create GPO
The onboarding file can be deployed with the use of GPO Scheduled Task.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console; right-click Group Policy Objects and create a new GPO
- Right-click this newly created GPO and then click Edit.
- Expand Computer Configuration and then go to the following path: Preferences -> Control Panel Settings -> Scheduled Tasks
- Right-click on scheduled tasks and then click New, and then click Immediate Task (At least Windows 7).
In the task window, go to the General tab and change the security options for the user or group. Type SYSTEM and then click Check Names. When correctly configured the user account; NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM appears as the user account. (1)

Select Run whether user is logged on or not (2) and check Run with highest privileges (3).
Go to the Actions tab and select New for adding the CMD script as part of the scheduled task. Configure the New Action for “Start a program” and use the fully qualified domain name of the shared locations. Don’t forget to include the correct script including the .cmd extension.
Locate for example directly to //FileShareLocation/WindowsDefenderATPOnboardingScript.cmd

Sample submission
Sample submission can be configured based on two ways;
- Import Group Policy Template directly to the C:\Windows\PolicyDefinitions or C:\Windows\PolicyDefinitions\en-US location or use the central store for Group Policy Administrative Templates. ADMX files are located in the OptionalParamsPolicy folder located in the downloaded onboarding package
- Configure Sample submission using a registry key
Sample submission GPO configuration:
After importing the GPO template configure the setting; Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Defender ATP and configure the setting: Enable\Disable Sample collection with the value Enabled

Sample submission registry configuration:
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Key path: SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Advanced Threat Protection
- Value name: AllowSampleCollection
- Value type: DWORD
- Value data: 1
For allowing sharing of all file types the value data is 1. It is recommended to enable sharing of all file types when using Defender for Endpoint. Value 0 Doesn’t allow sample sharing.
Troubleshooting
Available troubleshooting steps for tracking the SENSE onboarding and Configuration Manager Endpoint Protection profile for onboarding:
Sense event log
Defender for Endpoint generates multiple log files. During onboarding issues – the SENSE event log can be used for detecting the state.

Log locations:
- Onboarding: Event Viewer – Windows Logs > Application event source WDATPOnboarding
- Sense agent operational: Event Viewer – Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft -> Windows > SENSE > Operational
ATPhandler.log
When using Configuration Manager the ATPhandler.log can be used for additional troubleshooting on the police side.
Log locations:
- C:\Windows\CCM\Logs\ATPHandler.log
Conclusion
Part3D of the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint series is completed – focussed on the initial Defender for Endpoint onboarding using GPO en Configuration Manager for Windows 10/11 workstations. All parts for the initial Defender for Endpoint onboarding are completed and explained in parts 3A, 3B, 3C, and 3D. Stay tuned for the next parts; where more in-depth knowledge and experience will be shared around Defender for Endpoint focussing on the Defender AV configuration and additional protection settings.
Searching for specific Defender for Endpoint information? Use the contact submission form and share the post ideas or contact using Linkedin or Twitter. I will take all suggestions into the Defender for Endpoint series and help the community as far as possible.
View previous part – Microsoft Defender for Endpoint series – Onboard using Azure Arc – Part3C
View next part – Configure AV/ next-generation protection – Part4
Sources
Microsoft: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint – Endpoint Protection MECM
Microsoft: Onboard Windows devices using Group Policy
Microsoft: Onboard Windows devices using Configuration Manager



I dont get the new licensing model via DFC. I mean lets say we use Citrix non persistent SBC or VDI. How are we going to onboard those to Azure ARC and DFC and does Azure ARC / DFC even support non persistent ?
Interesting question – How is the non-persistent SBC or VDI OS version; is this based on Windows 10/11 or Windows Server 2016/2019+
SBC environment is a brand new Server 2022 environment.
Seems the best way for checking the licensing partner for these license-related questions. non-persistent SBC/ VDI is indeed really hard to be managed via Defender for Cloud.
There is still no official announcement for the standalone licensing option.