In all environments, reducing the vulnerability surface and getting insights into the vulnerable applications are recommended and important. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P2 contains the vulnerability management solution for getting visibility based on the installed MDE sensor.
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management (MDVM) is part of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint – there is no additional agent or configuration needed for getting data in MDE. MDVM is a built-in module in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P2.
When using Defender for Endpoint there are multiple ways to block vulnerable and or unwanted applications. Let’s explore the process of securing vulnerable applications. Ideally, there is a dynamic source where all application/ CVEs and vulnerability information is located. In terms of Defender for Endpoint this part of the product and included in Defender for Endpoint P2. An add-on is available with more features – including a feature for blocking applications based on the vulnerable version.
| Blog information: Blog published: April 5, 2023 Blog latest updated: April 5, 2023 |
Blog tip: Defender for Endpoint series (17 blogs)
Vulnerability Management plans
Microsoft Defender supports multiple offerings for Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management:
Defender for Endpoint P2:
- Core TVM capabilities included
Add-on for Defender for Endpoint P2:
- Defender Vulnerability Management add-on
Defender Vulnerability Management Standalone
- Full vulnerability management capabilities
Defender Vulnerability Management is explained in the recent MDE blog series more in-depth. More information: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint series – Defender Vulnerability Management – Part5
How can we block vulnerable applications?
Currently, there are multiple ways available to block applications. Common examples:
- AppLocker
- Block applications with the “Don’t run specified Windows applications” setting
- Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC)
- PUA (Potentially Unwanted Applications)
AppLocker/ Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC) is useful for blocking specific apps and controlling which applications, drivers, and certificates can run on Windows systems.
What is a vulnerable application?
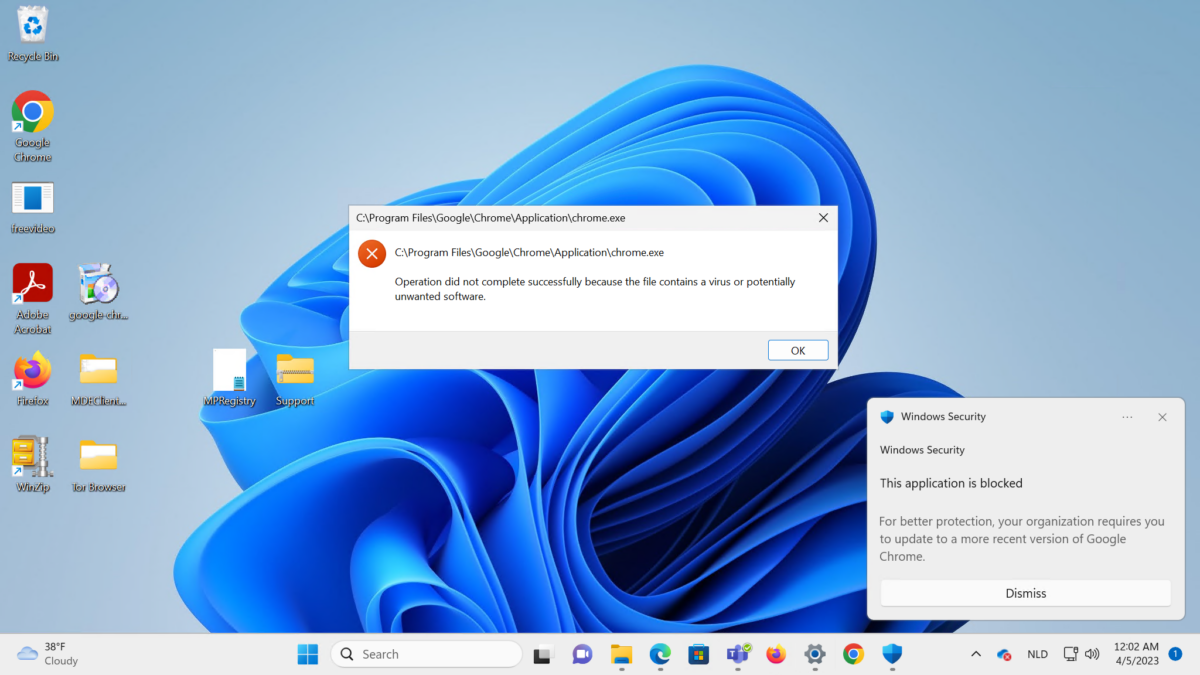
Application vulnerabilities are weaknesses in an application that an attacker could exploit to harm the application’s security. An example is CVE-2023-1217, and CVE-2023-1216 in Google Chrome.
Now the common question is; how can we block specific vulnerable versions of Google Chrome and allow only the recent non-vulnerable versions? In this situation, the new feature part of the Vulnerability Management add-on adds value for blocking specific versions based on the discovered inventory data.
Vulnerability Management add-on
Add-ons for Defender for Endpoint? Yes… The core Vulnerability features are included in MDE P2. For additional features, there is the add-on offering for Vulnerability Management. The Defender Vulnerability Management add-on for MDE P2 adds the following features:
- Security baselines assessment
- Block vulnerable applications
- Browser Extensions
- Digital certificate assessment
- Network share analysis
- Hardware and firmware assessment
- Authenticated scan for Windows
Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 2 includes access to the premium vulnerability management capabilities. The Vulnerability Management add-on is part of the Defender for Servers Plan 2 plan, no additional licensing/ cost is needed when servers are part of Defender for Servers Plan 2.
Block vulnerable applications
With the use of Defender Vulnerability Management functionality, it is possible to block all known vulnerable versions of the application. Before we use the feature it is important to validate the minimal requirements.
The blocking vulnerable application feature requires the following key components in Defender for Endpoint:
- Defender Antivirus in active mode. (EDR in block/ Passive is not working)
- Cloud-delivered protection enabled and configured
- Advanced Features allow or block file enabled

Make sure the version of the Defender Antivirus is up-to-date with one of the latest supported versions. The TVM blocking capability requires 4.18.1901.x or later – where the latest version is always recommended. Tip: Validate the version using the PowerShell command; Get-MpComputerStatus
| Important: Defender AV must be enabled and running in active mode. Blocking vulnerable versions is only working when the AV is running in active mode. |
Where to block specific apps?
When blocking apps it all starts in the security recommendations view for mitigating vulnerabilities. Use the remediation type filter “Software update/ Software upgrade“

In the above view the recommendation “Update Google Chrome to version 111.0.5563.65” is visible. Open the recommendation and click Request remediation.
In this situation, the vulnerable version 110.0.5481.180 is blocked.

When needed the remediation can be scoped to all device groups or specific groups. The remediation request is important for tracking the remediation process and improvement.
For software updates, the remediation option is “Software update” and configure the remediation due date, priority, and notes.

For supported software, there is the Mitigation action screen. With the mitigation action, it is possible to mitigate the risk and block/ warn all vulnerable versions of the applications from running.

When using the warn/ block action it is possible to inform the users. The message will appear when users open the vulnerable version of the application. By default Microsoft adds the following information link; aka.ms/TvmApplicationBlockSupport custom URLs can be configured in the notification.

After creating the remediation request all indicators of the known vulnerable applications are automatically configured in the indicator list as file hash. For Chrome the title contains “Blocked vulnerable Chrome versions”. Good to know the indicators are only added for the specific – the description field contains all information including the related software and version.

For each configured URL the title and description are automatically filled in with application details.

Remediation actions are not visible for all apps
This is correct – the remediation block/warn options are not visible for all apps. When the mitigation option is not visible the app is currently not supported. The following apps are not supported:
- Microsoft Applications
- Recommendations related to operating systems
- macOS/ Linux apps
- Apps where Microsoft does not have sufficient information or high confidence to block
View all blocked applications
Via the remediation page in Microsoft 365 Defender, it is possible to view all created remediations and blocked applications.

When opening the software page more detailed information is visible; including the number of blocked vulnerabilities, available exploits/ blocked versions and activities.

In the same view, it is possible to unblock the software and remove all affected indicators. Recommended is to keep the indicator list healthy and clean.

Blocked versions contain the actually blocked versions:

Result
After creating the remediation it takes up to 30 minutes before the policy has to be applied to all devices. Defender for Endpoint adds all indicators automatically as part of the file hashes.
When attempting to launch an application part of the blocked hashes; the end user will see a notification that this specific application was blocked. When “warn” is configured the user is able to bypass the block after the warning. The toast notification is visible with the block explanation – admins are able to add custom messages.
Block message

With the use of hunting/ Advanced Hunting, it is possible to view the policy results. Depending on the policy the ActionType is AntivirusDetection with the AdditionalField TVMBlock or TVMWarn.
DeviceEvents
| where ActionType == "AntivirusDetection"
| where AdditionalFields contains "TVMBlock"
DeviceEvents
| where ActionType == "AntivirusDetection"
| where AdditionalFields contains "TVMWarn"
Sources
Microsoft: Block vulnerable applications
Microsoft Tech Community: Mitigate risks with application block in Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management