Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP). Defender for Cloud contains a large set of features and capabilities; it is based on the following:
- DevSecOps solution (DevSecOps)
- Cloud security posture management (CSPM)
- Cloud workload protection platform (CWPP)
Introduction blog series
This ultimate blog series will contain as much information as possible based on my Defender for Cloud experience in the past years. Not a copy of Microsoft Docs, but an addition based on practical experience combined with informational details – including the most frequent questions asked by customers focussing on the configuration and deployment.
Specific question or content idea part of Defender for Cloud? Use the contact submission form and share the post ideas.
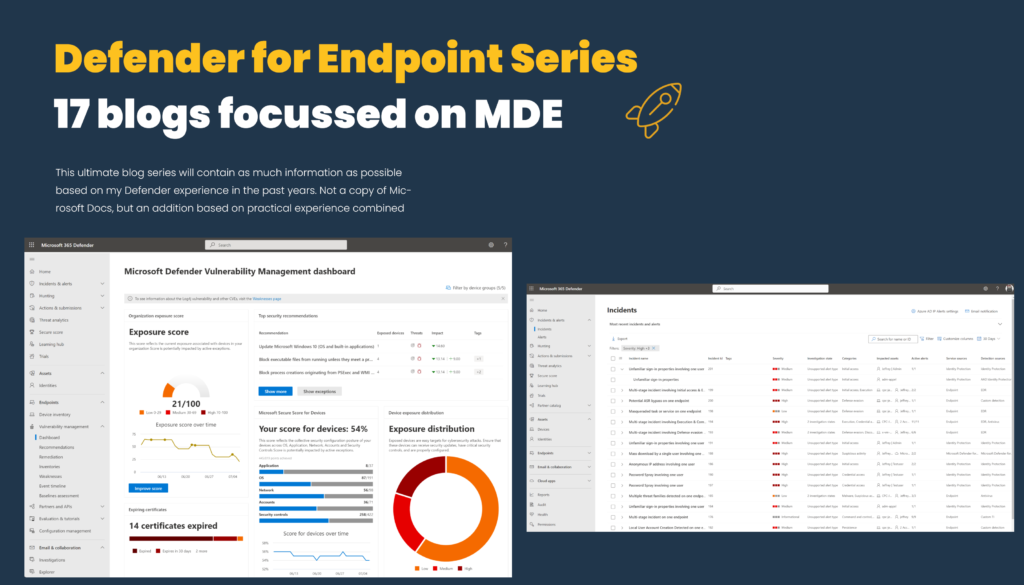
Previous MDE blog series
The first blog series published on my website is focused on Defender for Endpoint. View the Defender for Endpoint Series here (17 blogs focussed on MDE)

What is Microsoft Defender for Cloud?
Defender for Cloud helps in the prevention, detection, and response to threats and gives visibility into the security surface of the resources. Defender for Cloud is a complete solution with multiple enhanced protection features. Microsoft calls Defender for Cloud a security posture management and threat protection tool (CSPM/ CWPP)
Enhanced security features/ plans
Defender for Cloud contains more protection via separate Defender security features/ plans. Currently, the following enhanced security plans are available in Defender for Cloud:

Cloud Workload Protection (CWP)
- Foundational CSPM
- Defender CSPM
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
- Defender for Servers
- Defender for App Services
- Defender for Databases
- Defender for Storage
- Defender for Containers
- Defender for Key Vault
- Defender for Resource Manager
- Defender for DNS
Defender for Cloud solution
As you can see there are a couple of protections part of Defender for Cloud. For a good successful implementation, it is critical to configure the services/ components correctly. Monitoring and onboarding are important. Defender for Cloud collects data via a couple of tools. Some Defender plans require monitoring components to collect data from your workloads. Defender for Cloud collects data via:
- Azure Monitor Agent
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE)
- Log Analytics agent (MMA)
Data collection is required and possible via multiple monitor agents (AMA vs MMA). Without a provision agent, there is a limited set of security and capabilities. In this new blog series, all components will be explained including the data collection/ subscription configuration and usage.
Stay tuned for the first blog post in this new series focusing on the introduction of the Defender for Cloud platform.
Part of the Defender for Cloud blog series
View all the published parts of the Defender for Cloud blog series:
- Part 0: Microsoft Defender for Cloud– The ultimate blog series (Intro)
- Part 1: What is Defender for Cloud and how works the product/ service
- Part 2: Requirement of the monitoring components
- Part 3: Enablement of the protections
- Part 4: ………
- Part 5: ………
- Part 6: ………
All related blogs are part of the MDC-Series post tag, view the overview page.
Contribute
Is there something missing? Use the contact submission form and share the post ideas or contact using Linkedin or Twitter. I will take all suggestions into the Defender for Cloud series and help the community as far as possible.




I am looking forward to the continuation of the series 🙂
Hi Denis; thanks – working on the next blogs – all waiting for some changes from the private channels to be announched in public.
I think Cloud workload protection and CSPM components should be interchanged in the above article.